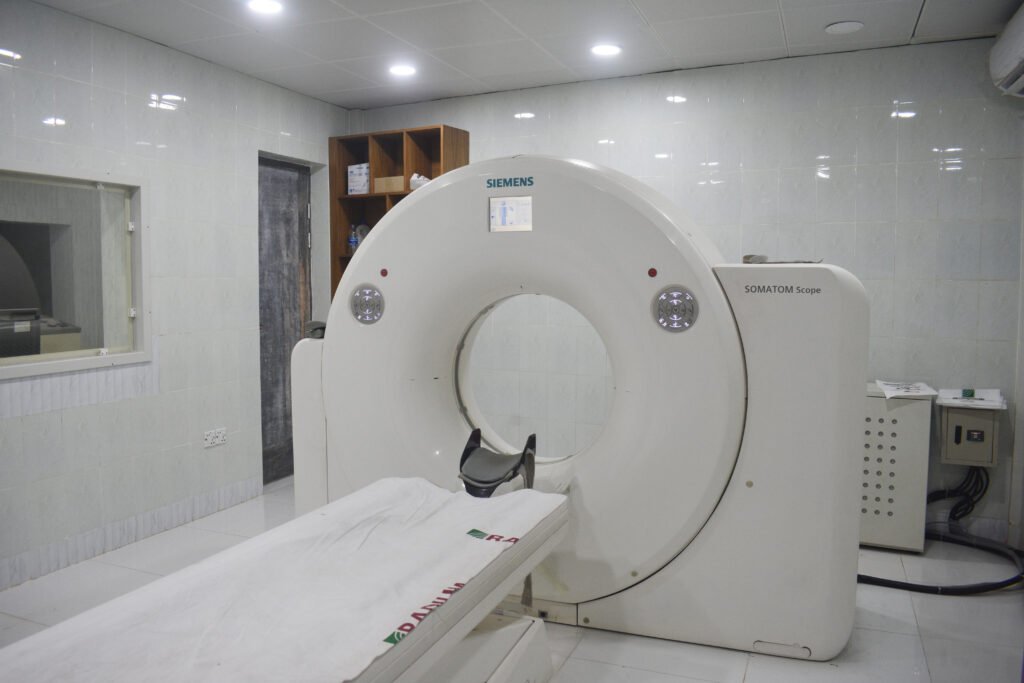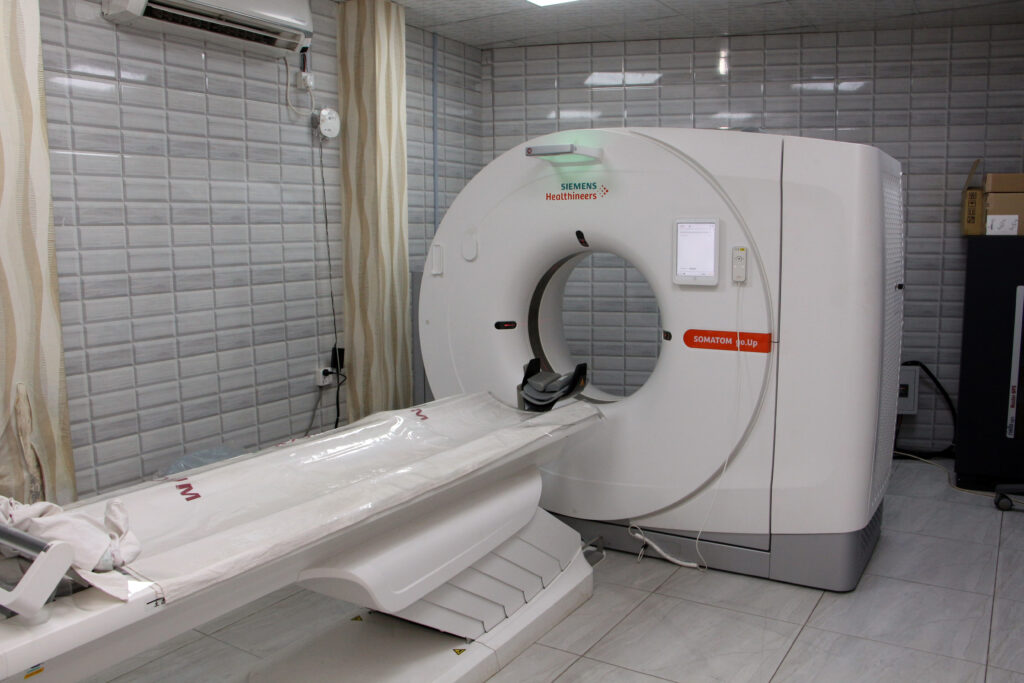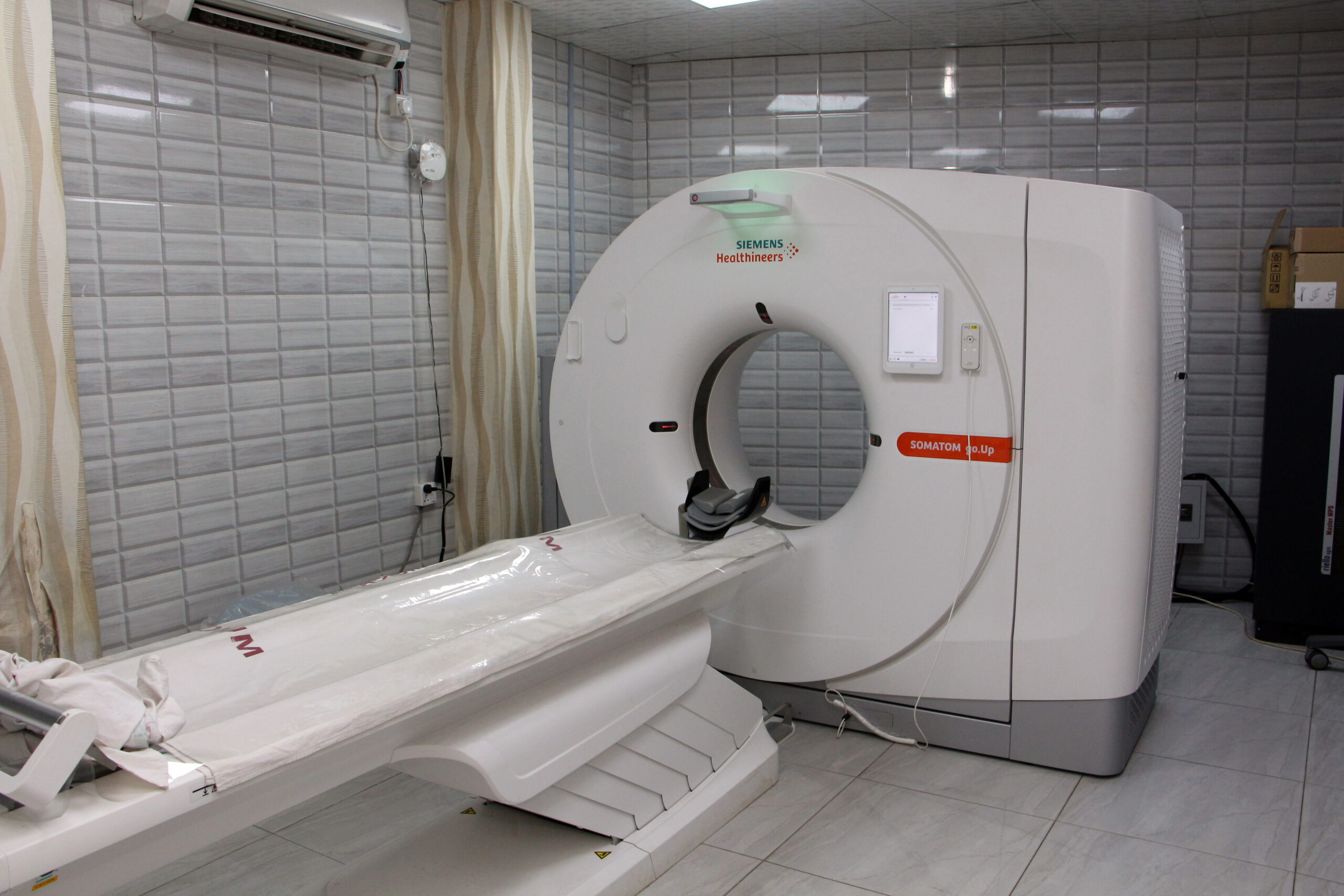
Spiral CT (Computed Tomography) scan Diagnosis
A Spiral CT (Computed Tomography) scan, also known as a helical CT scan, is a medical imaging procedure that combines X-ray technology with computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. This diagnostic test is often used to visualize internal structures, organs, and tissues in the body. Here’s a brief description of a Spiral CT scan which is the best point Radium Diagnostic Center in Gazipur: Procedure: During a Spiral CT scan, the patient lies on a table that is slowly moved through a doughnut-shaped machine called a CT scanner. The scanner consists of an X-ray tube and detectors that rotate around the body. The X-ray tube emits a series of narrow, fan-shaped X-ray beams, and the detectors record the amount of X-rays that pass through the body from different angles. Helical Scanning: Unlike traditional CT scans, which acquire images one slice at a time, a Spiral CT scan uses continuous rotation and a helical path to capture data in a spiral fashion. This results in faster imaging and the ability to create 3D reconstructions. Data Acquisition: As the scanner rotates, it captures a large volume of data. This data is processed by a computer to create cross-sectional images (slices) of the body. These images are highly detailed and can be viewed in various planes, such as axial (cross-section), sagittal (side view), and coronal (frontal view). Diagnostic Applications: Spiral CT scans are used for a wide range of diagnostic purposes. They can detect and evaluate conditions such as tumors, injuries, infections, blood clots, and structural abnormalities in various body parts, including the head, chest, abdomen, pelvis, and extremities. They are particularly valuable for assessing the lungs, detecting pulmonary embolisms, and diagnosing various cancers. Contrast Enhancement: In some cases, a contrast dye (iodine-based contrast material) may be administered intravenously to enhance the visibility of blood vessels, organs, and abnormalities. This is especially common in abdominal and vascular CT scans. Patient Preparation: Depending on the specific area of the body being scanned, patients may be instructed to fast for a certain period before the procedure. They may also need to remove metal objects and inform the healthcare provider of any allergies to contrast material. Safety Considerations: While Spiral CT scans provide valuable diagnostic information, they involve exposure to ionizing radiation. Healthcare providers aim to use the lowest radiation dose necessary to obtain the required images, especially in the case of repeat or pediatric scans. Post-Processing: The CT scan data can be reconstructed into 3D images, which can be manipulated for a more detailed view of the area of interest. These images can aid in surgical planning and treatment decisions. Spiral CT scans are a versatile and powerful diagnostic tool that can provide valuable insights for medical professionals in diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of medical conditions. However, it’s important to use them judiciously, as they do expose patients to ionizing radiation, and the benefits should outweigh the potential risks in each case. Radium is the best place for this diagnosis test as easy and safely.
- Treats minor illnesses
- Answers health questions
- Conducts health checkups
- Specialty physicians
- Performs routine health tests
- List Items
1000 +
Operations done
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting.
Spiral CT Scan diagnosis test information
A Spiral CT (Computed Tomography) scan is a diagnostic imaging test that provides detailed cross-sectional images of the body using X-ray technology. Here’s more information about the Spiral CT scan: Spiral CT vs. Conventional CT: Spiral CT, also known as helical CT, is an advanced version of the conventional CT scan. In a conventional CT scan, the X-ray machine and the patient’s table stop and start for each image slice. In contrast, Spiral CT continuously rotates the X-ray machine and table, creating a continuous helical path, which allows for quicker image acquisition and 3D reconstruction. Procedure: During a Spiral CT scan, the patient is positioned on a table that moves through the donut-shaped CT scanner. As the table moves, the X-ray tube within the scanner rotates around the patient, emitting X-ray beams. Detectors on the opposite side of the patient measure the X-rays, and a computer processes the data to generate detailed cross-sectional images. Diagnostic Applications: Spiral CT scans are versatile and can be used to evaluate various body parts, including the head, chest, abdomen, pelvis, and extremities. Common diagnostic applications include: Lung Imaging: Spiral CT is often used for lung cancer screening and to diagnose pulmonary conditions. Cardiac Imaging: It can assess coronary arteries and evaluate heart function. Abdominal Imaging: Spiral CT can help detect and diagnose issues in the abdominal region, such as tumors, kidney stones, and abdominal aortic aneurysms. Vascular Imaging: It is used to visualize blood vessels and detect vascular diseases. Trauma Evaluation: Spiral CT is valuable for assessing injuries after trauma, like fractures and internal bleeding. Cancer Staging: It aids in determining the extent of cancer and whether it has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes. Contrast Enhancement: In some cases, a contrast dye may be administered intravenously (contrast-enhanced CT) to improve the visibility of blood vessels and organs. This is common in abdominal and vascular CT scans. Patient Preparation: Depending on the specific type of Spiral CT scan, patients may need to follow certain preparations. This can include fasting for a specified time before the procedure and informing the healthcare provider about any allergies or previous adverse reactions to contrast material. Safety Considerations: Spiral CT scans involve exposure to ionizing radiation. To minimize radiation exposure, healthcare providers strive to use the lowest radiation dose necessary to obtain high-quality images, especially for repeated scans and when imaging children. Post-Processing: The data from Spiral CT scans can be reconstructed into 3D images, providing a more comprehensive view of the area being examined. This is particularly useful in surgical planning and in understanding complex anatomical structures. Spiral CT scans have revolutionized diagnostic imaging, offering rapid, high-resolution images that can aid in the early detection and precise diagnosis of various medical conditions. However, the use of ionizing radiation requires careful consideration of the potential risks and benefits for each patient. These scans are typically performed in hospitals or specialized imaging centers and are interpreted by radiologists and other healthcare professionals.
Spiral CT Scan diagnosis test
A Spiral CT (Computed Tomography) scan is a diagnostic imaging test that provides detailed cross-sectional images of the body using X-ray technology.
Why need spiral CT scan
Spiral CT scans, also known as helical CT scans, are used for a variety of diagnostic purposes when healthcare providers need detailed, cross-sectional images of the body.
How to Spiral CT Scan
A Spiral CT (Computed Tomography) scan is a medical imaging procedure that is performed by a trained radiologic technologist or radiographer.